Have a full house working, gaming, streaming, and binge-watching news all at once? If you’re experiencing lag or slow internet, try these simple troubleshooting tips before calling your ISP.
With more smart home devices, cloud gaming, and video streaming services than ever, a stable internet connection is essential. If you notice lag while playing League of Legends or music downloads crawling to a halt, the issue is often on your end—not necessarily your internet service provider. So, what’s causing the problem? Before scheduling a service call, follow these step-by-step troubleshooting tips to get your internet connection back on track quickly.
1. Test Another Device or Website
First, determine the scope: Is the issue limited to one device or affecting all your devices? If only one device has problems, the issue is likely with that machine. If multiple devices experience trouble, your network may be the culprit.
Try accessing a different website. If some sites load fine but one doesn’t, the website itself may be down. Use services like downforeveryoneorjustme.com or downdetector.com to check for known outages. If no outage is reported, clear your browser’s cache, try a private browsing window, or switch browsers to rule out browser issues.
2. Verify Your Internet Speed
Is your internet slower than expected? Run a speed test on Speedtest.net to measure your actual download and upload speeds. Then compare these numbers to what you’re paying for on your ISP bill. If speeds match your plan but feel slow, consider upgrading. If speeds are significantly slower, continue troubleshooting.
3. Check Wi-Fi Settings
Make sure your device is connected to the correct Wi-Fi network (SSID). On Windows and older macOS versions, prioritize your preferred network or disable auto-connect on unwanted ones.
If connected correctly but experiencing issues, use built-in network troubleshooters—right-click your network icon on Windows and select “Troubleshoot problems” or “Diagnose network problem.” These tools can fix common issues by resetting your network adapter. Also, verify adapter settings to ensure your device uses the correct gateway.
4. Monitor Bandwidth Usage
Background apps can consume bandwidth, slowing your connection. On Windows, open Task Manager (Ctrl-Shift-Esc) and sort by network usage. On macOS, use Activity Monitor’s Network tab.
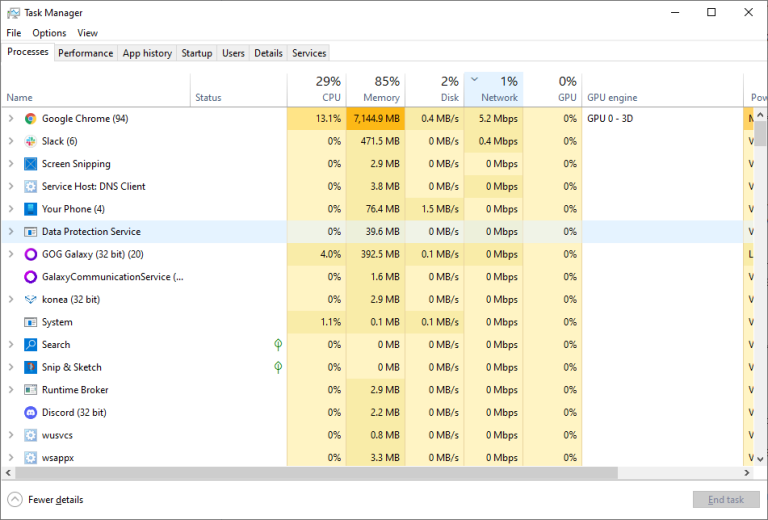
If one app or device is hogging bandwidth—perhaps a large download or game streaming—wait for it to finish or pause the activity. Check if someone else in your home is using lots of data, and consider setting bandwidth limits or Quality of Service (QoS) rules on your router. Also, watch out for unauthorized users stealing your Wi-Fi; tools are available to identify and remove them.
5. Scan for Malware
Malware, spyware, and viruses can degrade your internet speed and overall system performance. Run a full virus scan with Windows Defender or trusted antivirus software. Mac users should also use reputable antivirus programs, as Macs are not immune to threats.
6. Change or Reset DNS Settings
Your DNS server translates website names to IP addresses. If DNS servers have issues, websites may fail to load. Try flushing your DNS cache or switching to a reliable public DNS server like Google DNS or Cloudflare DNS, either on individual devices or your router.
7. Interpret Your Modem and Router Lights
LED indicators on your modem/router convey vital info. If some lights are off or flashing irregularly, consult your device manual for their meaning. For example, Wi-Fi lights off may mean Wi-Fi is disabled; press the Wi-Fi button or enable it via settings.
If no lights come on, check power cables and switches. Power cycle by unplugging the modem/router for a minute, then plug in the modem first, followed by the router. Persistent issues may be due to faulty power adapters or hardware.
8. Improve Wi-Fi Signal
Poor Wi-Fi signals cause slow speeds. Connect directly using an Ethernet cable to test if Wi-Fi is the problem. Relocate your router centrally in your home or eliminate obstructions. Use Wi-Fi extenders or mesh networks to improve coverage.
If nearby networks cause interference, switch channels or use the 5GHz band for less congestion.
9. Update Firmware
Router and modem performance can be enhanced with firmware updates. Access your router’s settings to check for firmware updates from the manufacturer’s official source. Updating can fix bugs, improve speed, and add features. Mesh systems often allow updates via their apps for convenience.
10. Reset Router Settings
If you’ve changed router settings and problems started afterward, perform a factory reset. Usually done by holding a small reset button on the back until lights flash. Then set up the router from scratch through its web interface.
11. Consider a Router Upgrade
Older routers using outdated standards (802.11b/g) may not handle multiple devices efficiently. Consider upgrading to a dual-band or tri-band router with the latest Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E standard for improved speed and range. Wi-Fi 7 exists but is not yet widely adopted.
12. Inspect External Cables
Examine the main cable into your home for damage, loose connections, or wear. Replace rusty or dirty cable splitters and tighten all connections, as poor physical connections degrade signal strength.
Final Step: Contact Your ISP
If all else fails, the problem may lie with your ISP’s equipment or service. Contact them for support or equipment replacement like a new modem or amplifier. Slowdowns during peak hours could mean your ISP is struggling with capacity—consider switching providers if needed.
By following these comprehensive tips, most internet issues can be diagnosed and resolved without professional help, keeping your streaming, gaming, and work flowing smoothly.